+86-159 9860 6917
info@geofantex.com
geofantex@gmail.com
+86-400-8266163-44899
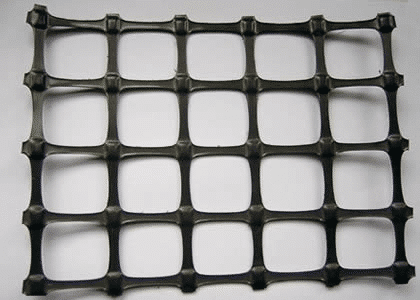
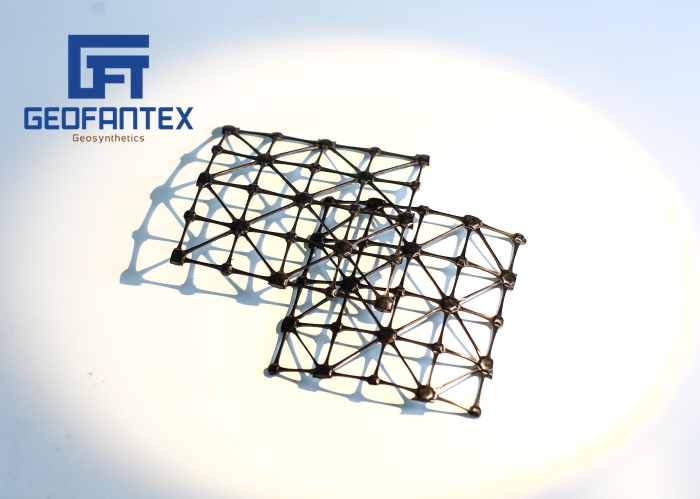
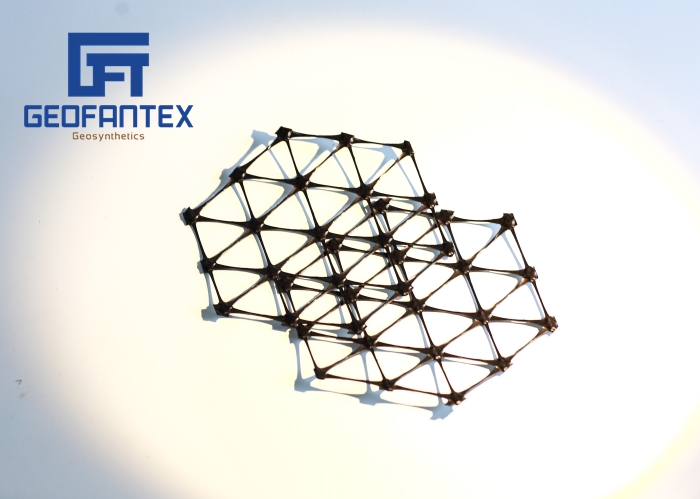
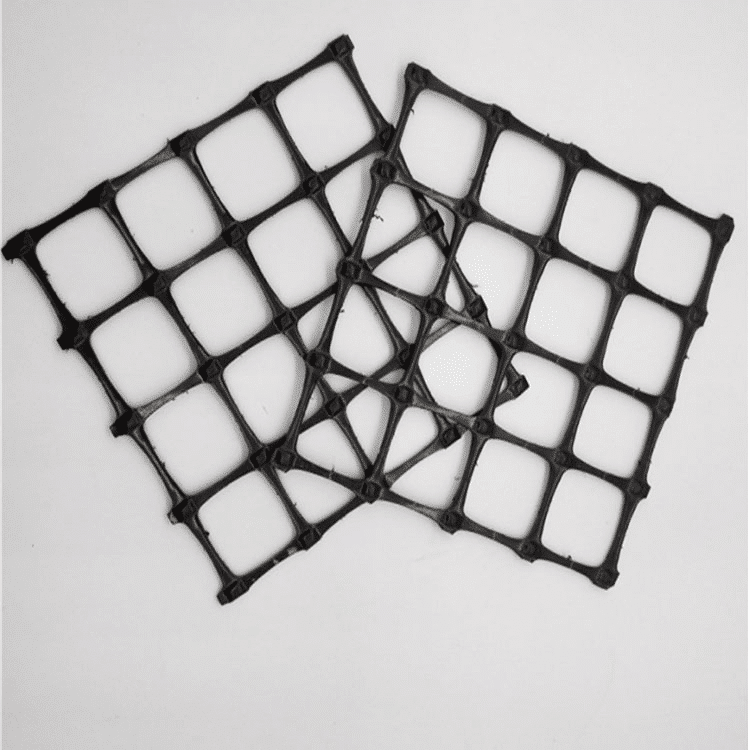
Geomalla plástica biaxial
La geomalla está construida con polímeros perforados o extruidos y tiene un alto nivel de durabilidad. El uso de una rejilla biaxial puede servir como medida preventiva eficaz contra las fuerzas erosivas.
¿Qué es la geomalla biaxial?
A biaxial geogrid is a type of geosynthetic material used predominantly in civil engineering and construction projects. Its main function is to reinforce soil and stabilize ground in applications such as roadways, parking lots, and foundations.
Composition: Biaxial geogrids are typically made from polymers such as polypropylene or polyester. They are characterized by their grid-like structure, consisting of ribs that intersect at right angles. This configuration allows for strength and stiffness in both the longitudinal and transverse directions, hence the term “biaxial.”
Characteristics:
- High tensile strength: The material is designed to resist stretching under stress, providing effective soil reinforcement.
- Flexibility: Despite their strength, biaxial geogrids are flexible enough to contour to varying landscapes.
- Durability: These geogrids are resistant to biological degradation and chemical interactions with the soils, making them suitable for long-term applications.
Applications:
- Road construction: They are used to improve the load-carrying capacity of the roads by distributing loads over a wider area.
- Soil stabilization: Helps prevent soil erosion in slopes and embankments.
- Foundation support: Increases the stability of building foundations by reinforcing the ground.
Biaxial geogrids provide a cost-effective solution for enhancing soil stability and are integral to modern geotechnical engineering.
El diseño biaxial les permite distribuir cargas de manera más efectiva y aumentar la vida útil de la estructura donde se implementan. Al integrarla en un proyecto, la geomalla interacciona con el material de relleno (como grava o tierra), creando una matriz más cohesiva y resistente. Esto ayuda a prevenir problemas como el hundimiento o desplazamiento del terreno bajo cargas pesadas.
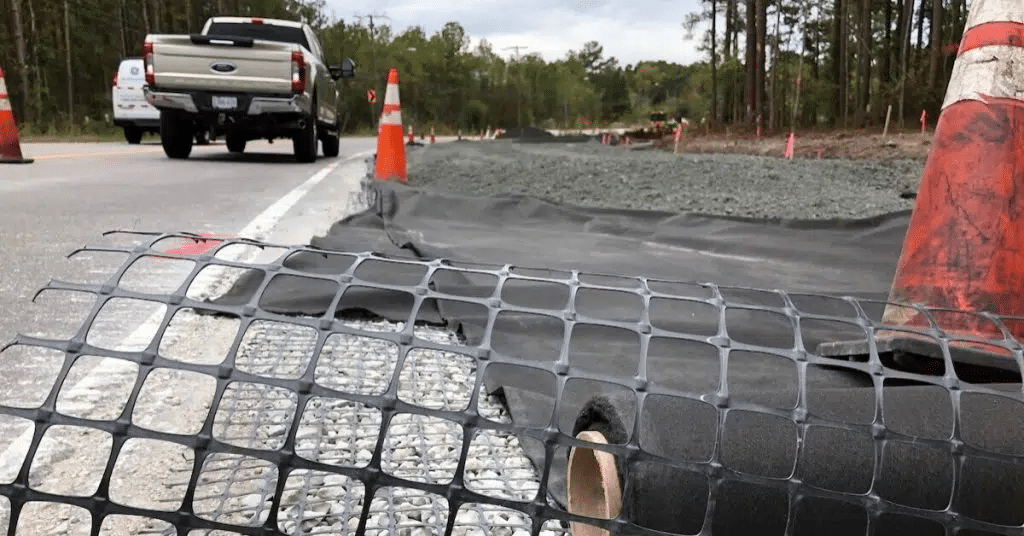
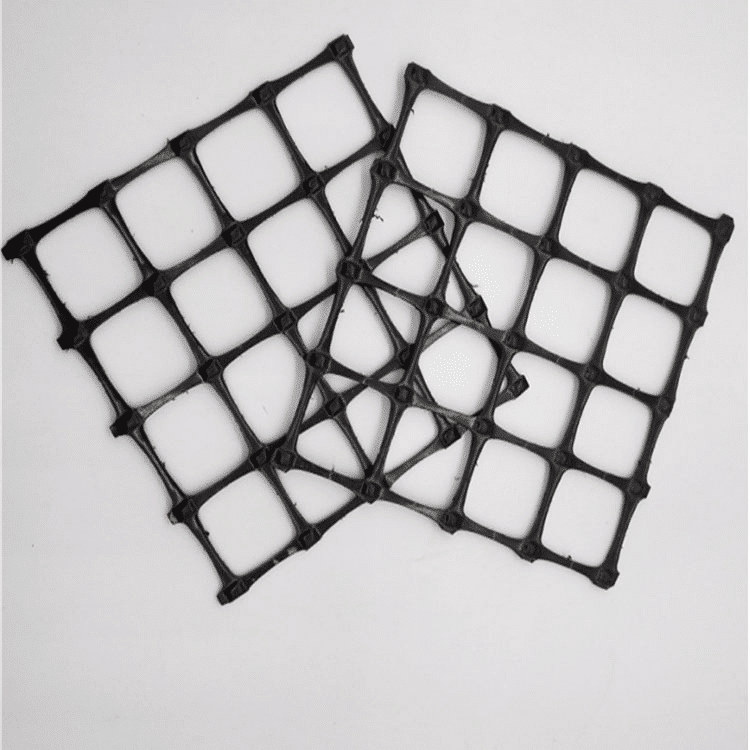
¿Cuáles son las aplicaciones de la geomalla biaxial?
Las geomallas biaxiales son estructuras de refuerzo fabricadas generalmente de polipropileno, poliéster o polietileno, que se utilizan ampliamente en la ingeniería civil y construcción. Estas geomallas tienen una serie de aplicaciones importantes gracias a su resistencia en dos direcciones (biaxial), lo que las hace ideales para distribuir cargas de manera uniforme en superficies extensas. Aquí te detallo algunas de sus principales aplicaciones:
Refuerzo de pavimentos:
- Las geomallas biaxiales se usan para aumentar la vida útil de los pavimentos al mejorar la distribución de las cargas vehiculares sobre la sub-base del pavimento. Esto reduce las deformaciones y el agrietamiento.
Construcción de carreteras:
- En la construcción de carreteras sobre suelos blandos, las geomallas ayudan a estabilizar el terreno, distribuir uniformemente las cargas y mejorar el rendimiento estructural del camino.
Refuerzo de cimentaciones:
- Se utilizan para mejorar la capacidad de carga y reducir los asentamientos en cimentaciones, especialmente en suelos con baja capacidad portante.
Construcción de muros de contención y taludes:
- Las geomallas biaxiales se emplean para estabilizar muros de contención y taludes, proporcionando refuerzo adicional que permite construir estructuras más estables y seguras.
Control de la erosión:
- Se aplican en la protección de taludes y áreas propensas a la erosión para prevenir la pérdida de suelo y promover la vegetación al estabilizar el terreno.
Aplicaciones en ferrocarriles:
- Utilizadas bajo las vías del tren para mejorar la estabilidad y distribución de cargas, reduciendo el mantenimiento y prolongando la vida útil de la infraestructura.
Urbanización y desarrollos residenciales:
- En desarrollos urbanos, las geomallas biaxiales pueden utilizarse para estabilizar suelos y crear bases sólidas para carreteras, aceras y otras infraestructuras.
Estas aplicaciones demuestran la versatilidad y eficacia de las geomallas biaxiales en una variedad de proyectos de construcción y de ingeniería civil, donde la estabilidad del terreno y la distribución eficiente de las cargas son esenciales.
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre geomalla biaxial y uniaxial?
Biaxial and uniaxial geogrids are important materials used in civil engineering projects, particularly in soil stabilization and reinforcement. Here is a detailed comparison of their characteristics, applications, and performance:
Structural Characteristics:
- Uniaxial Geogrids: These are designed to stretch primarily in one direction. Their strength is optimized in the longitudinal direction, which is crucial for applications where load directionality is significant.
- Biaxial Geogrids: In contrast, biaxial geogrids can stretch and provide strength in two directions—both longitudinal and transverse. This makes them more versatile in resisting stresses from multiple directions.
Applications:
- Uniaxial Geogrids: Commonly used in retaining walls and steep slopes where the primary stress is in one direction. They help in retaining soil under tension and managing lateral pressures.
- Biaxial Geogrids: These are often applied in roadway and pavement construction, and under foundations where ground forces are multidirectional. Their ability to distribute loads evenly makes them ideal for these applications.
Performance in Soil Reinforcement and Stabilization:
- Uniaxial Geogrids: They are effective in enhancing the mechanical stability of earth structures by reinforcing the soil in a preferred direction, often leading to improved bearing capacity and reduced deformation.
- Biaxial Geogrids: These geogrids help in increasing the soil’s confinement and aggregate interlock, which enhances the overall stability of the soil matrix. This results in improved load-carrying capacity of the soil and prevents differential settling.
Advantages and Limitations:
- Uniaxial Geogrids: Advantages include high tensile strength in one direction, which is beneficial for vertical structures like walls. However, their limitation lies in less flexibility to adapt to multidirectional stresses.
- Biaxial Geogrids: They offer flexibility and effectiveness under multidirectional stresses, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. The limitation may include a potentially higher cost due to more complex manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, the choice between biaxial and uniaxial geogrids depends on the specific requirements of the project, including the direction of expected loads and the desired outcomes in terms of soil stability and reinforcement.
¿Cuál es la diferencia entre geomalla biaxial y triaxial?
Geogrids are materials used in construction and civil engineering to reinforce soil and other materials. Biaxial and triaxial geogrids are two types of such materials, each with distinct characteristics and applications.
Structural Characteristics:
- Biaxial Geogrids: These have a structure that is reinforced in two directions, typically at 90 degrees to each other. The grid structure is often square or rectangular. Biaxial geogrids are made from materials like polypropylene or polyester, designed to distribute loads over a wider area.
- Triaxial Geogrids: Triaxial geogrids are reinforced in three directions, making them isotropic (uniform in all directions). Their structure typically consists of a hexagonal or triangular grid. This design allows for more effective stabilization of soil by evenly distributing forces in multiple directions.
Applications:
- Biaxial Geogrids: Commonly used in road construction, parking lots, and embankments where the main loading direction is known and primarily two-dimensional.
- Triaxial Geogrids: More versatile due to their isotropic nature. Ideal for applications requiring multidirectional load distribution such as railway track beds, steep slopes, and areas with soft soil that need uniform stabilization.
Benefits and Limitations:
- Biaxial Geogrids:
- Benefits: Effective at distributing load horizontally, good for two-directional stabilization.
- Limitations: Not as effective in applications where forces are applied from multiple directions.
- Triaxial Geogrids:
- Benefits: Provides uniform load distribution, enhancing soil stabilization under varied stress conditions.
- Limitations: Generally more expensive due to the complexity of their design and manufacturing process.
In summary, the choice between biaxial and triaxial geogrids depends largely on the specific engineering needs of the project, considering factors like soil type, load direction, and budget constraints.Cuando se trata de un alto contenido de humedad, las geomallas se pueden usar junto con geotextiles para evitar que los tipos de suelo se mezclen, lo que puede hacer que disminuya la relación de soporte del núcleo del suelo.








Obtenga una muestra gratis
We’ll respond as soon as possible(within 12 hours)